How Empathy Is Key To Creating Phenomenal Experiences For Our Users
User Research; Empathize and Define. Understanding your user and the problem you are trying to solve.
Hello, So its my second week in UI/UX course through FemCode Africa. Its been a great experience and i am sharing it with you my readers.
Outlines;
- Empathize with users
- Build an empathy map
- Understand user problems
- Explore personas
- Write user stories
- Identify happy paths and edge cases
- Discover benefits of user journey maps
- Consider accessibility
- Write problems statements and hypothesis statements
User experience research focuses on understanding user behaviors, needs and motivations through observation and feedback. The goal of a user experience researcher is to prioritize the user and meet business needs.
• UX research can help bridge the gap between what a business thinks the user needs and what they actually needs, before an expensive and time-consuming product is made.
• UX research fits into the Products Development Life cycle which is the process used to take a product from an idea to reality. UX research is a continuous part of a products development life cycle and it takes place before, during, and after the design stage.
Types of User Research
Research that takes place before a product is designed is called foundational research or strategic research it is also known as general research. Foundational research gives answer to questions like; i. What should we build? ii. What are the user problems? iii. How can we solve them?
Design research is a type of research that takes place during the design stage. It is also called tactical research and provides answer to questions like; i. How should we build it? ii. How was the users experience using the prototype?
Post -launch research happens at the end of a products development life cycle. It is used to evaluate how well a launch feature is meeting the needs of the user. It gives answers to the question; Did we succeed?
Key Qualities of a UX Researcher
- Empathy: you should be able to understand someone else's feelings or thoughts in a situation
- Pragmatism: A UX researcher should be focused on reaching goals
- Collaboration: He's someone who can work with a wide range of people, personalities and work styles.
User Research Method
There are two categories to user research method. It’s based on;
a. Who conducts the research; primary and secondary research Primary research is a research you conduct yourself using surveys, interviews or conducting a usability study to hear directly from the user. Secondary research is research that uses information provided by others. This could be gotten from books, journals, articles. This is done at the beginning of product development life cycle.
b. The type of data collected; quantitative and qualitative Quantitative data is gotten by counting or measuring and answers questions like; how many and how much. Qualitative type of data is based on observation, interviews and requires smaller number of users. It answers the why and how.
USER RESEARCH METHODS
- An interview is a type of research method used to collect in-depth information on people's opinions, thoughts experiences and feelings. it is always open ended and requires detailed response.
- Survey is an activity where many people are asked the same questions in order to understand what most people think about a product. It is a mixture of qualitative and quantitative data.
- A usability study is a technique to evaluate a product by testing it on users. The goal is to identify user pain points and experiences with different prototypes. If the product is already launched, a post launch usability study might include data like key performance indicators also known as KPIs which is a critical measure of progress towards an end goal. For example, The KPI's for a new product launched include; how much time the user spent on a task or number of times they make a purchase. The research method we choose is determined by the question we are trying to answer.
The Benefits and Drawbacks of User Research Methods
- A new product requires a secondary research first to know the statistics, facts and figures that already exist and this saves time and money because you do not need to redo a work that is already done. It is simply accessible using the Internet and it is in turn used to back up the primary research. One of the drawbacks is that there is no first hand user interaction since the researcher does not make direct contact with the users. Hence, no specific user feedback.
- Interview method helps to understand what users think and why they think so. Follow up questions could possibly be asked. Its drawback is that it is time consuming because participants are interviewed one after the other and it is expensive. It also involves smaller sample size hence limits the information collected.
- Survey type of data always involves larger sample size. It preserves time and also inexpensive. One of the drawbacks is that feedback is limited (no in depth feedback from the user)
- Usability study offers first hand user interaction and challenges our assumptions on the users experience when using our product. it also provides in-depth feedback from the user. Its drawbacks is that it is highly expensive also time consuming
Designer bias in UX research that affects design work and how to overcome them
A. Confirmation bias occurs when tries to prove a hypothesis he has by searching for evidence. Confirmation bias can be overcome by conducting open-ended questions and actively listening to a user. A large sample of users should be included as well.
B. False consensus bias is the assumption that others will think the same way you do. It happens when we overestimate the number of people who will agree with our idea or design. You can overcome it by identifying and articulating your assumptions as well as surveying a large group.
C. Recency bias is when it is easiest to remember the last thing you heard in a conversation or interview which is overcome by taking detailed notes.
D. Primacy bias is just the opposite of recency bias. When you are in a new situation or having a new experience, you tend to remember the first person or participant you meet and feels he makes the strongest impression. It can be overcome by taking detail notes or recordings and also interviewing each participant the same way so as to get varied experience.
E. Implicit bias or unconscious bias is the collection of attitude and stereotypes we associate to people without our conscious knowledge. Its common form is when we only interview people within a limited set of identity profile such as race, sex social status. Overcome Implicit bias by reflecting on your own behaviors.
F. Sunk costs fallacy is the idea that the deeper we get into a project we have invested so much time in, the harder it is to change course without feeling like we failed or wasted time. We can overcome it by breaking down projects into smaller phases.
Approaching user experience research with empathy makes it easier to solve the right problem. One way to visualize empathy is by creating an empathy map which explains everything designers have learned about the user. An empathy map is a chat contains what the user thinks, says, does and feels which is used determine if a problem is actually a problem as well as the pain points. Supposing a food delivery app that promises 30 minutes or less delivery is designed by your team and the users are interviewed about their experiences on the prototype
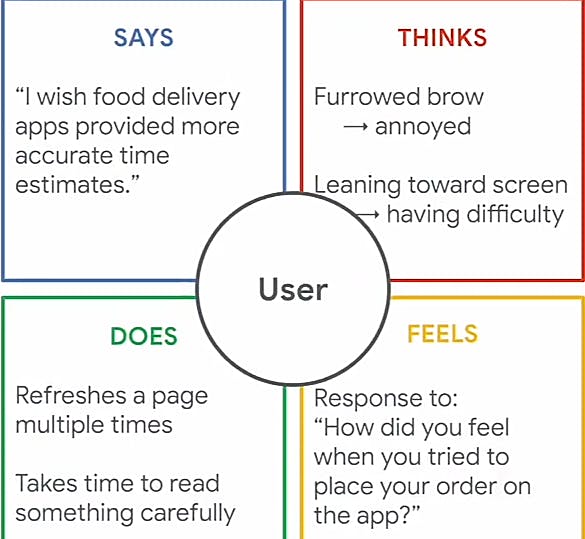
Ux designers are problem solvers. Pain points are any user experience issues that frustrate the user and blocks the user from getting what they need.
Types of pain points
- Financial pain points
- Product pain points
- Process pain points
Support pain points
financial pain points are pain points related to money. A user experiences this type of pain points when using a website and gets rudely interrupted by an ad.
Product pain points have to do with the users experience on the issues of quality of the product like Norman doors, if you expect a door to open, it should open.
Process pain point is identified when there is a no smooth process to achieving a goal. A user who shopped online but struggles to get the item he wants to check out undergoes process pain points.
When a user is on a website but finds it impossible to navigate through the website and is not able to find a support link, or sends a message to the support team but gets no response. It is quite frustrating and this could be identified as a support pain point.
Empathy maps help us get into the users mindset and that is why designers create Personas.
Personas
Personas are fictional users whose goals and characteristics represent the needs of a larger group of users. It can help us identify patterns of behavior in users and this patterns might point to a particular pain point that a group of user experiences. In building a persona, one has to find out what user group your persona represents. A user group is a set of people who have similar interest, goals or concerns.
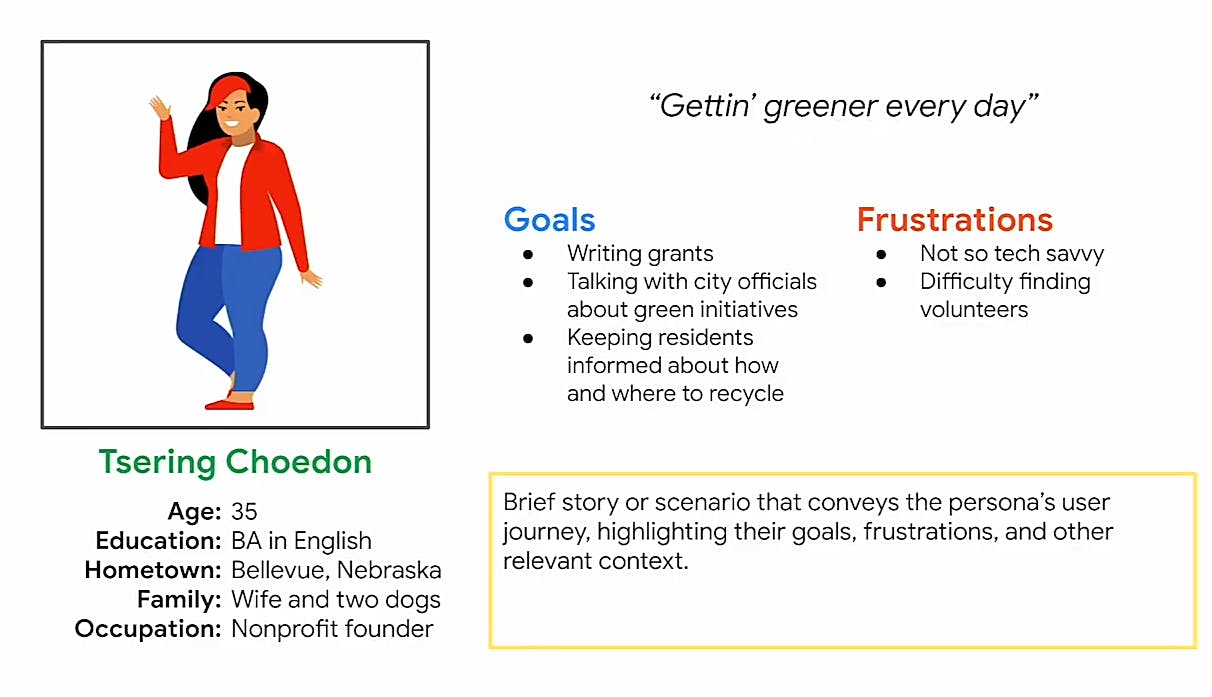
Let’s say we are designing a fund raising app that connects nonprofits with volunteers. One of the user groups might be owners of environmental nonprofits in rural areas and our persona would be Tsering Choedon, the founder of ourplanet.org. In other words, Tsering Choedon stands in as a persona for owners of environmental nonprofits (user group)
Each persona created humanizes a user group for the team. Tsering's goals and frustrations could be seen below
Personas are not imagined but real users. A major importance of persona is that it tells a user story which is a fictional one sentence story told from a personas point of view to inspire and inform design decisions. User story introduces the user (who), lays out an obstacle (action), and states ultimate goal (benefit). To write a user story using persona, we should consider the who, the what, and the why
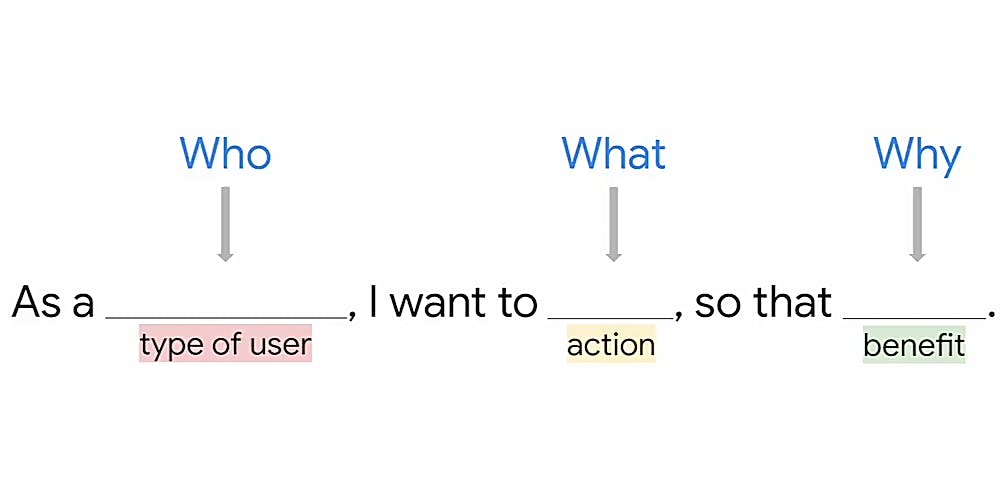
An example of user story
As an online shopper (who) I want to receive a text (what) when the item arrives so that I can pick it up (why).
Personas and user stories are also created In order to help spot and resolve edge cases so as to channel a user to a happy path. Edge cases are what happens when things go wrong that are beyond the users control why using a particular product while happy paths describes a user story with a happy ending.
Wireframes are also used to identify pain points of potential users. It helps to visualize the project which makes it easier to identify pain points and fix them
User Journey
User journey is the series of experiences a user has as they interact with your product. It builds off the persona and stories you have created. They help you think and feel like the user because if you can't put yourself in the users shoes, you can't be sure your design will really help them. Just like every other journey, you need a direction. User journey requires a user journey map which is an illustration of what the user goes through to achieve their goals. When we want read a book; if our persona is the character, user story is the plot and journey map is the story outline which guides you as you read the book.
- User journey Maps help the ux designer to create obstacle-free paths for users
- It Highlights new pain points and also create room for identifying improvement opportunities.
supposing your persona, ROSE is BI-RACIAL and wants to fill out a form but does not see a drop down menu that lets her answer, she hits a road block and gets frustrated because there is no option to identify herself as both black and Korean. a pain point is identified and can be improved by adding a drop down menu for users to write in their racial identity.
How to map out a user’s journey
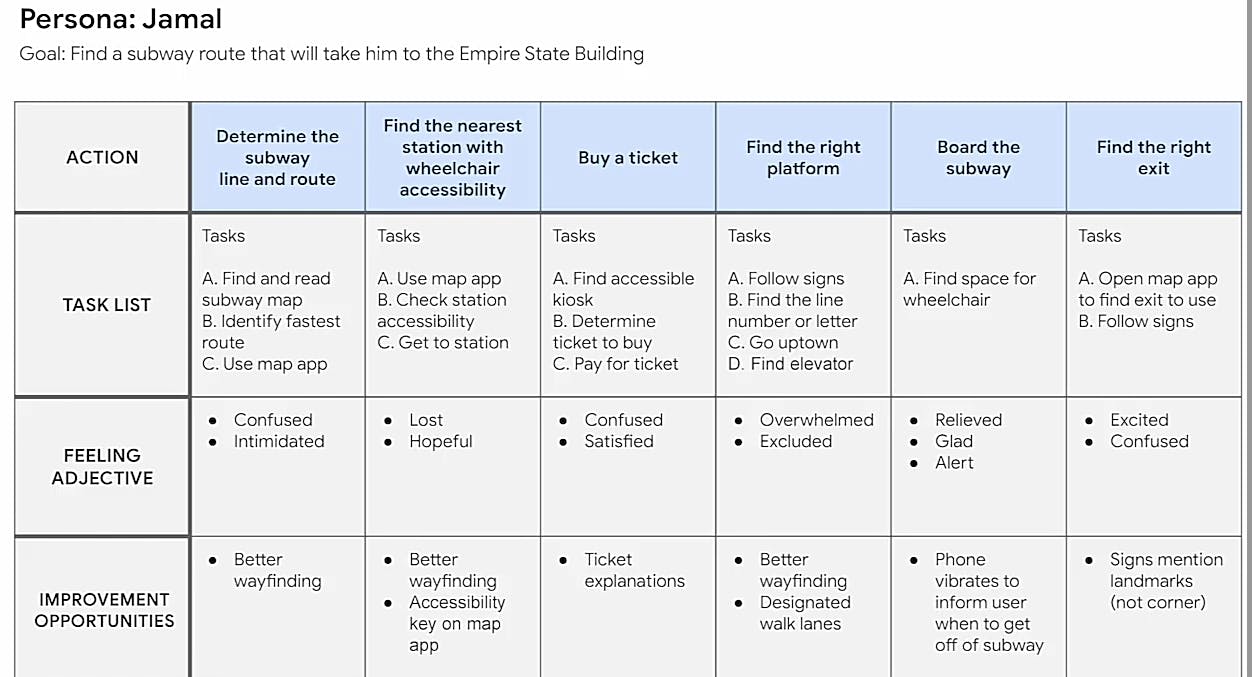
Supposing a man named Jamal is a persona who uses a wheelchair to get around and is visiting New York City for the first time. John wants to fulfill his dream of going all the way to the top of the Empire State Building.
Let’s map out his journey
- Firstly add each action in the journey until the user reaches their goal which is to find a subway route that will take him to the Empire State Building
- Add descriptions for each action stating what tasks the user have to do
- Include the users feelings at each point
- Add opportunities for improvement. This can also give room for new ideas
The strength, height and disability of a user should be put into consideration while designing a product.
Accessibility
Accessibility is the design of products, devices, services or environments for people with disabilities. However accessibility is not just designing to include a group of users with varying abilities. It also extends to anyone who is experiencing a permanent, situational or temporary disability.
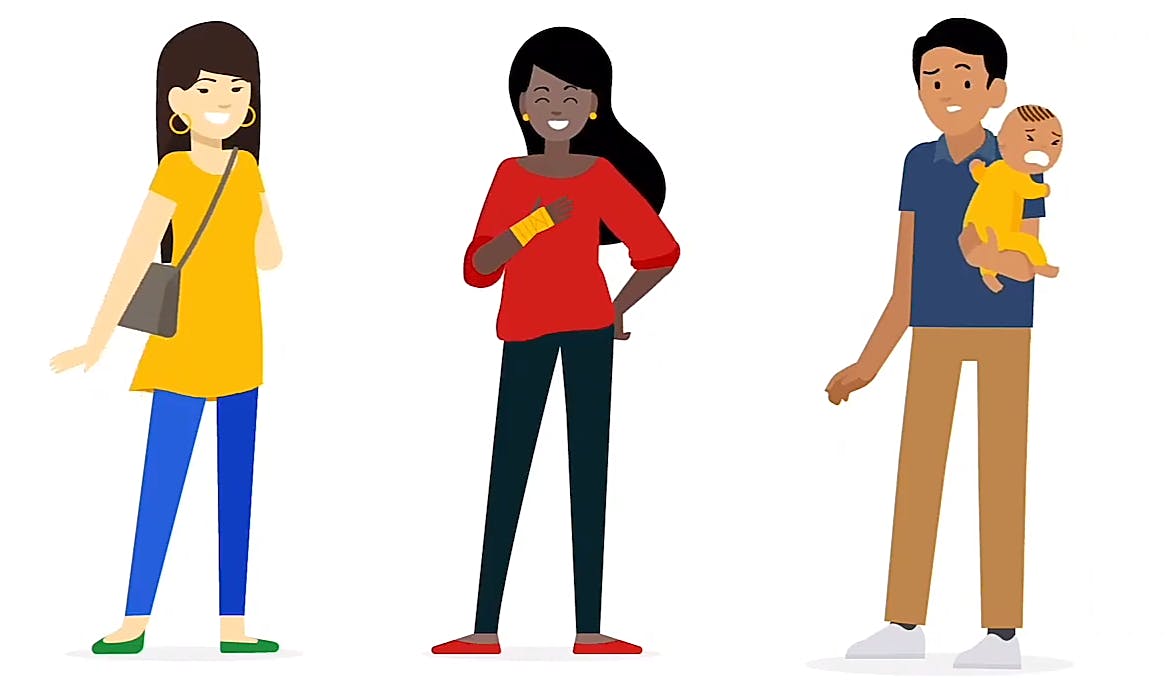

We can see the lady with a broken arm(permanent disability), another lady with a sprained wrist(temporary disability) and a man holding a new born(situational disability). They all need to achieve their goal with only one arm.
Designing for accessibility has also ended up favouring everyone else. The curb cut is a good example.
Curb cut is a name for the loop of the side walk that creates a ramp with the adjoining street, which are usually found at intersections. people with wheelchairs, leg braces, clutches easily navigate their neighborhood but the benefits of curb cut extends to everyone; to people pushing strollers riding bicycles ,elderly people as well etc.

Generally Design exists to solve users problem. To start defining a design problem we need to synthesize everything in the empathy stage; pain points and personas, user stories and user journeys.
Problem Statement
A problem statement is a clear description of users needs that should be addressed
A problem statement should be;
- Human centered
- It is also broad enough for creative freedom but should also be narrow enough to be solved by a design solution
The benefits of problems statement
- It helps to establish goals because defining the goal clearly and concisely helps everyone on the design team to be focused on the same thing
- It also helps to understand constraints, what is keeping users from satisfying their needs
- It defines deliverables, it is helpful to know what our solution will produce
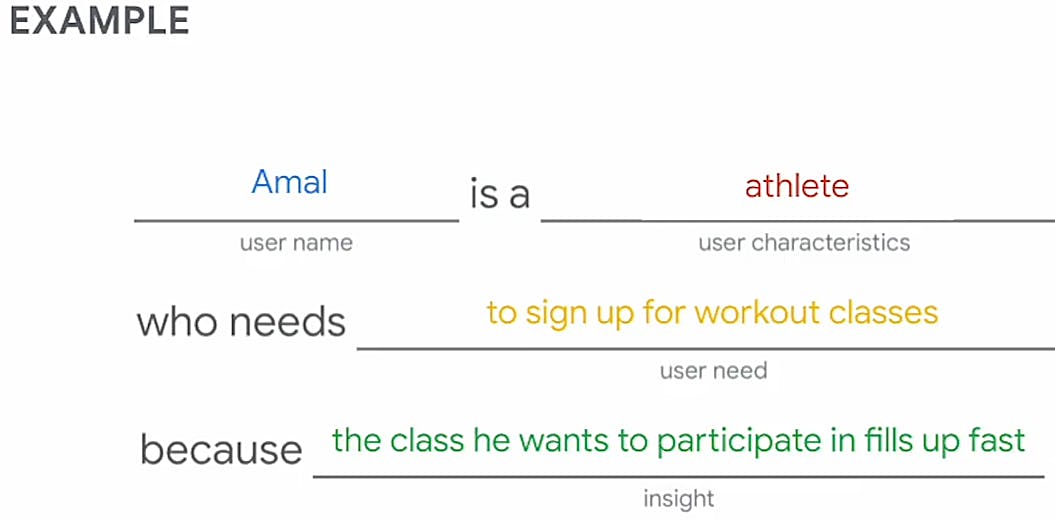
- It creates benchmarks for success. How will we know when we succeed? If a users goal is to open a door you will know you have succeeded when you see what is behind the door Next step is to brain storm solutions, right down possible solutions and ideas conceived. This is called a hypothesis statement which is our best educated guess, what we think the solution to a design problem might be.

Another idea could be; Amal needs an app that allows his preserve his favourite classes in advance and notifies him of the first opportunity to sign up.
In the design process, you will revisit and adjust your hypothesis as you learn more about users needs. Be flexible and adapt as you progress in order to come up with the best solutions.
Thanks for reading!

